GeoAssign
The Web based program assigns test individuals according to their genotypes or metric traits to groups (e.g. country of origin, population of origin) which are defined by reference individuals. Thus the user needs to upload one data file for the test individuals (“Test file”) and one data file for the reference individuals (“Reference file”). The assignment is done using a nearest neighbour approach (Degen et al. 2017, doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.fsigen.2016.12.011).
Structure of the user interface
The user interface is subdivided in three parts:
-
Upload area for input files
Running the GeoAssign server requires two files: one file (in the following called "test file") that contains data of samples whose origin has to be verified /assigned. The other file (in the following called "reference file") contains the reference samples which are already grouped into populations. You can upload your test and reference file by clicking the corresponding buttons in the upload area. The file format is described in the following section. As a third step, the input data type has to be selected, you can choose between genetic data and metric data like isotopic ratio data. -
Area for calculation details
Here, you can adjust the calculation details.
Percentile of most similar individuals (0.1 - 20%): This parameter controls the number of nearest neighbours (reference individuals with small genetic/ metric distance between test individual and reference individual). It is a percentile of all reference individuals ordered according to their genetic / metric distance to the test individual.
Minimum proportion of complete loci / traits (0.1 - 1): Often the data of genotypes or metric traits of the test individuals and reference individuals are incomplete. Missing data are coded by “-1”. This parameter determines which proportion of missing data can be tolerated. E.g. if you select as parameter “0.8” only test individuals and reference individuals will be included in the calculations when they have data for at least 80% of their genotype or metric traits. -
Output file details area
The GeoAssign program has two output modi: in the default case, it only generates summary data on the asignment. If you uncheck the "Print only summary files", on additional file for each test sample wil be generated. For more information about the output files, go to the output file section.
The "Prefix for output files" field gives the user the opportunity to choose a prefix for all output files.
After completion of the calculation you get an email containing a download link for your results. Therefore, it is necessary to specify an email address.
Input data files
The input files are simple ASCII files. They can be created with any commonly used editor. (Note: The program requires points "." as separator of decimal places (e.g. "125.12"). If you are not using the UK or US regional configuration make sure that your operating system support this setting.) The file content consits of a header part and a data part. The header part provides a small amount of numbers needed for the assignment calculation. The data part is line based, each line represents one sample. Variables are separated by “,”. Missing data are indicated by “-1”. The format for the reference and the test file is identical and explained in the following figures:
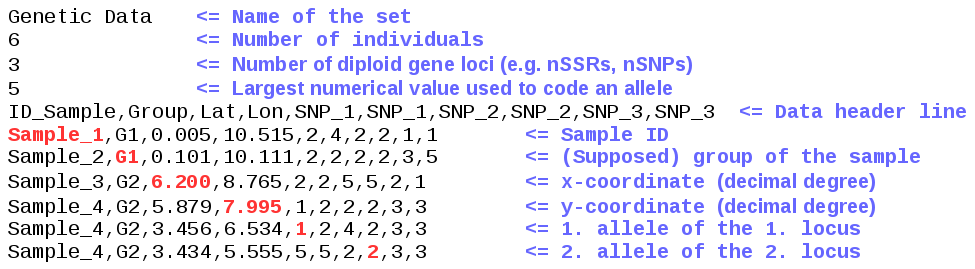

Note: For a successfull GeoAssign calculation, it is essential that the header and the data header line of test and reference file are identical!
Explanatory notes on the different fields:
- Header: The name of the data set can be any string. The number of individuals has to be equal to the number of sample lines in this file. The number of diploid gene loci (for genetic data) or the number of quantitative traits has to correspond to the number of these fields in the file. Please note: in case of genetic data, each gene loci consists of two alleles! The different alleles must be coded by numerical values. There is no restriction in terms of number of alleles.The highest number has to be specified in the header (see Figure 1).
- Data header line: The order of the different data fields is fix and has to be identical to the order in the example above. The number of loci / traits is not restricted. Each locus name has to be duplicated in the header line.
- Data (Sample) line:
- Sample ID: The Sample ID has to be a string containg alphabetic characters, numbers, underscores and whitespaces.
- Group of the sample: In the test file, the assumed group membership for the individual is denoted. In the reference file, this field gives information about the group mempership of this individual.
- Coordinates: The coordinates define the location of the individual. The notation has to be in decimal degrees for longitude and latitude!
- Loci or traits: Alleles must be coded by numerical values. Missing data are indicated by “-1”. Each locus consists of two alleles. Haploid data can be entered as homozygotes. Other traits, like isotopic ratio, are single values.
Output files
The programme computes four different types of output files. The file names are composed by the user defined prefix and a suffix specific for each file type:
| Name | Content |
|---|---|
|
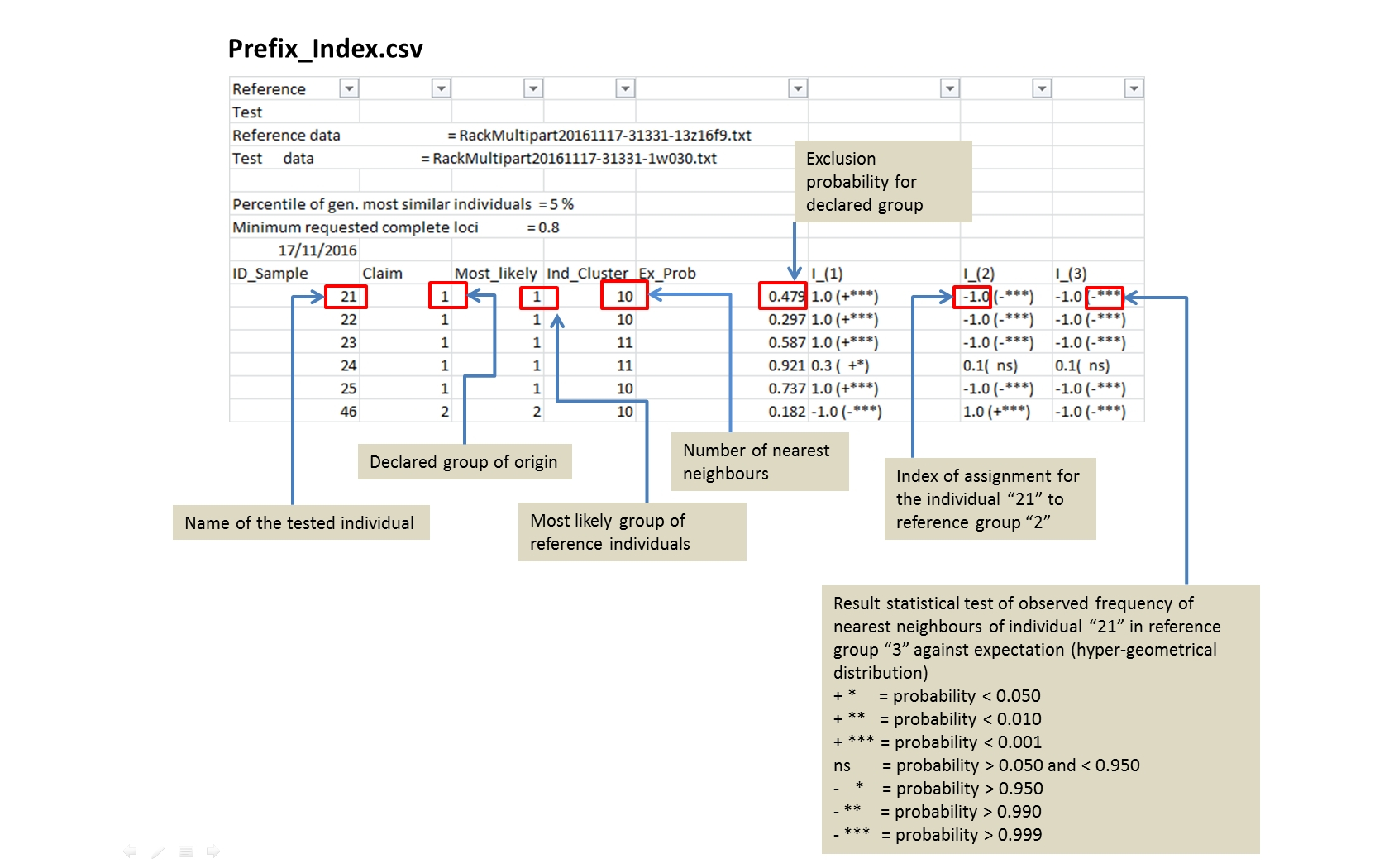
prefix_Index.csv Toggle details |
For each tested individual the values of the assignment indices in the different reference groups. The index represents the proportion of the nearest neighbours weighted by size of the reference group. |
|
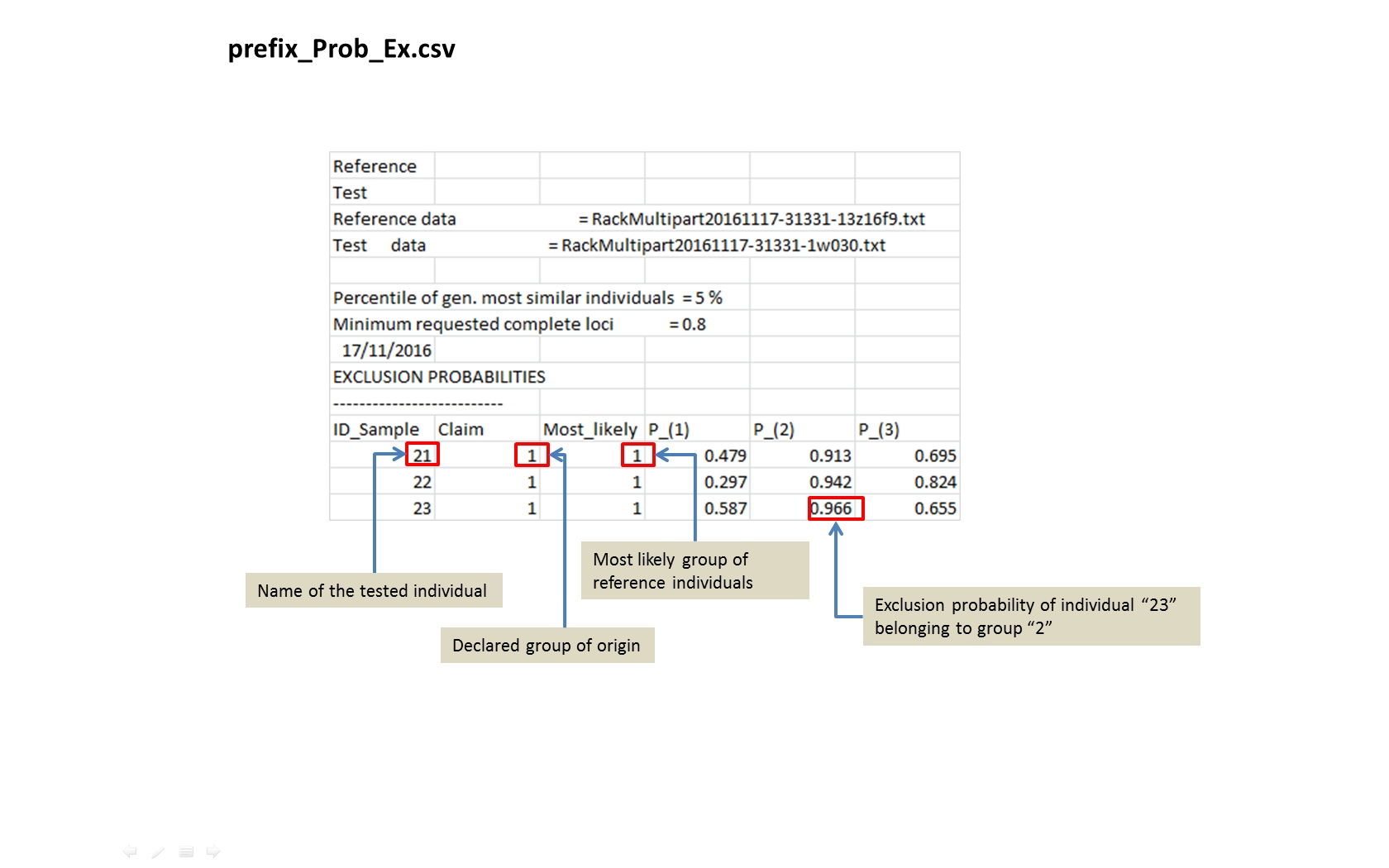
prefix_Ex_Prob.csv Toggle details |
For each tested individual the values of the exclusion probabilities in the different reference groups. As an indicator of exclusion (outlier) the programme computes the relative frequency of the smaller genetic/metric distances among pairs of individuals in each reference group compared to the distances among test and reference individual) |
|
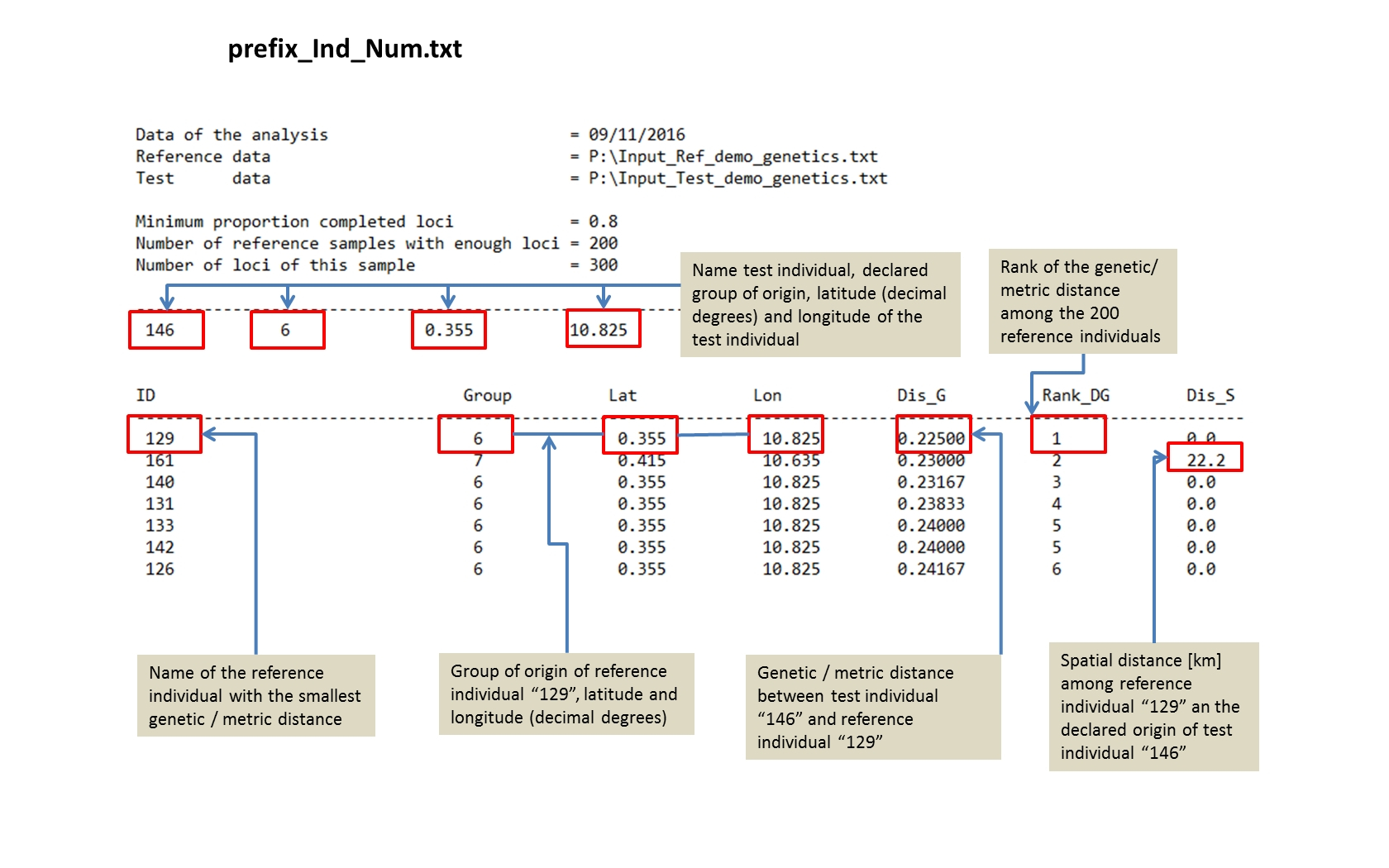
prefix_Ind_Num.txt Toggle details |
An ASCII text file for each tested individual “Ind_Num” with the genetic/metric distance among the test individual and all reference individuals ordered from the smallest to the largest distance. |
| prefix_Indentical_Genotypes.csv | This file is only optionally generated for genetic data. It includes a list of reference individuals with identical genotypes |
Further questions
If you have further questions or comments on the GeoAssign web server, please contact us.
© 2026 GeoAssign web server, Version 0.4.1.